User experience (UX) is a critical process applied when designing front-end of web platforms. Essentially, it is the process that design teams use to make products that offer relevant and meaningful experiences to users. This comprises of integrating the product into digital platforms through the aspects of functional design, branding, usability, and function.
Those who work on UX are called the UX designers. They research and evaluate how users feel about front-end digital system – evaluating such elements for ease of use, perception about the value of the system, efficiency, and utility in task performance.
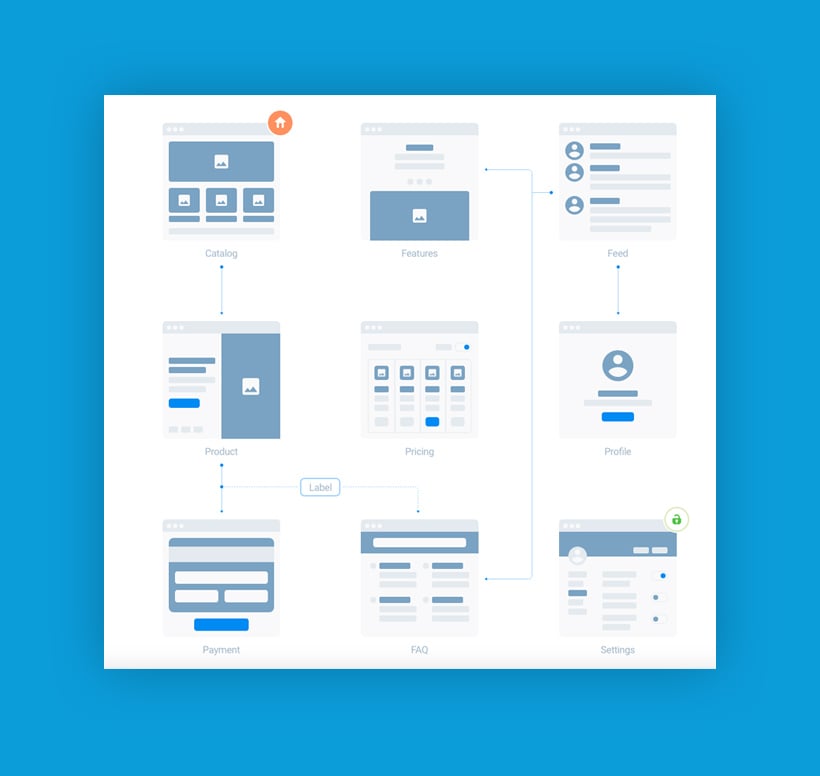
Design of UX
Since user-experience design covers the complete user end-to-end journey, it is considered to be a multi-disciplinary field. UX designers can emerge many walks of professional life, such as programming, psychology, visual design, and graphic design. When designing front-end user experiences, it pays to be sensitive. Users come from all the walks of life and require different guides to understand information. It is crucial to keep in mind about accessibility, along with accommodating to physical restraints of many potential users such as being color-blind.
The project scope of a UX designer varies, although it mostly includes design research, creating personas, interactive prototypes, and wireframes and also testing these designs. Even though these tasks may vary to a great extent from one organization to the other, it is core value of UX designers to be the user advocates and keep the users’ requirements central to the development and design efforts. UX designers keep directing their best-informed efforts until they optimally address all the relevant issues and requirements of potential users.
UX designers also look at the sub-systems and processes in a within a digital platform. For example, they might study the checking out process of an eCommerce website to evaluate whether the users find the buying process easy and pleasant from the website. They could probe deeper by studying various components of the digital platform’s sub-system like evaluating how pleasant and efficient is the users’ experience in filling input fields of a web form.
Why Care?
UX is crucial since it attempts to fulfill the user’s needs in navigating through a digital platform. UX connects your users with your products and services, thereby fulfilling your users’ requirements while simultaneously allowing your business to reach its goals. With the digital burst, much weight has been placed on the user-centric design as it has been tied with customer experience. Customer experience then translates to sales, which can be broken down into expanding the pipeline and retaining existing users.
This fact can be further re-enforced by research studies done. One study done by Baymard for 9 years on cart and checkout UX reveal that 69.2% of customers abandon a cart after adding items and the main reason for that is poor design and checkout flow.
Thus, improving UX will enhance customer experience and engagement, and in doing so will increase conversions and revenue.
Forecasting UX
The good news here is that UX is to stay. Establishments have started to understand and appreciate the importance of their customers’ impressions of their brands. With better customer experience, customers will build their trust and loyalty towards the brand.